Introduction
A lot of the work of the early chemists was aimed at identifying elements by finding differences between them, rather than looking for similarities. However, about 200 years ago, scientists realised that some elements were similar to each other and could be grouped together. Since then, many scientists have contributed to what has become the modern Periodic Table of the elements.
You will learn about the organization of the periodic table and the different elements. At the end of your journey through history, you will be able to recognise that metals and other elements are organised into the periodic table by their physical and chemical properties.
Elements are the basis of all life. Everything is made from elements. Scientists have been discovering and studying elements for hundreds of years.

Task
Your job is to look into the history of the atom, finding out information about elements, scientists and the periodic table
You will answer the following questions about the history of the atom and periodic table and at the end construct a timeline.
All work must be completed in your books with headings and tables drawn where appropriate.
Once completed, hand in for marking.
Atom Basics: Go to: http://www.chemtutor.com/struct.html and read the “And you thought you were strange” section to answer the following questions (put answers in the table).
1. What are the three subatomic particles that all atoms are made of?
2. Where are each of the three particles located within the atom?
3. What is the electrical charge of each particle?
| 1. The 3 Subatomic particles | 2. Location within the Atom | 3. Electrical Charge |
Early Ideas About Atoms: Go to http://galileo.phys.virginia.edu/classes/252/atoms.html and read the section on “Early Greek Ideas” in order to answer the following questions:
4. What was the “basic idea” about matter that Leucippus and Democritus proposed?
5. How did they use atoms to explain different physical properties?
6. How were the ideas of these two men received by Aristotle, and what was the result on the progress of atomic theory for the next 2,000 years?
John Dalton’s Atomic Theory: Go to http://www.iun.edu/~cpanhd/C101webnotes/compositio
7. When did Dalton form his Atomic Theory?
8. What are the four components of Dalton’s Atomic Theory?
J.J. Thomson and the Electron: Go to http://www.chemheritage.org/classroom/chemach/atomic/thomson.html and use the information there to answer the following questions:
9. What is the year in which J.J. Thomson discovered the electron?
10. What was the evidence for “bodies much smaller than atoms”?
11. What was the model of the atom he proposed in 1904?
Rutherford and Bohr Break the “Plum Pudding” Model:Go to http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/aso/databank/entries/dp13at.html and use the information found there to answer the following questions:
12. What was the “plum pudding” model of the atom and its electrons?
13. How much smaller was the nucleus, than the atom itself, according to Rutherford?
14. How did Bohr modify this model of the atom (i.e. what was his “revolutionary idea” about electrons)?
Chadwick (and Rutherford) and the Neutron Go to http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/aso/databank/entries/dp32ne.html and use the information found there to answer the following questions:
15. What makes up the atomic number?
16. What makes up the atomic mass?
17. What observation led Chadwick (and Rutherford) to conclude there must be something besides just the proton in the nucleus of atoms?
18. What is the something-besides-just-the proton called?
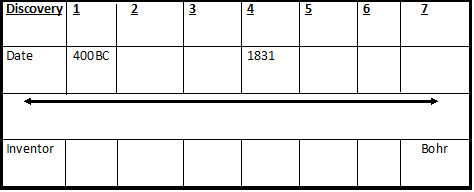
History of the Atom Timeline
Go to the folowing link: http://atomictimeline.net/index.php
Use the information in this web page to fill in your History of the Atom Timeline.
Use the following clues to help you. Make sure that all of the dates and all of the inventors are filled in.
Hints:
1. My famous quote was disputed by Aristotle, although time proved me correct.
2. In what date was it determined that matter can neither be created nor destroyed. Name the date and the scientist
3. Name the date and inventor of the modern version of the Atomic Theory
4. I was born in 1831 and showed that electricity and magnetism are scientifically related.
5. he developed the plum pudding model and also was the first to discover the ________ .
6. In 1909 this scientist demonstrated that the atom is mostly empty space with a small positively charged nucleus containing most of the mass and low mass negatively charged particles orbiting this nucleus. He was also credited with naming ______ and ______ .
7. What date did Neils Bohr developed the first successful model of the atom?
History of the Atom Timeline