Introduction
Etymology: Greek words Geo- "earth", -metri "measurement" -- "Earth-measuring"
Geometry is useful. As one might guess, geometry is used in advanced mathematics, such as it being applied in engineering and many skill trades. Geometry also enables one to learn what it means to prove a statement; generally, one will learn the ways of judging whether a bit of reasoning is true or not. More importantly, geometry provides a way of understanding the nature of mathematics as it is a logically organized subject.
Finally, the study of geometry is fun. There is a thrill in learning new knowledge.
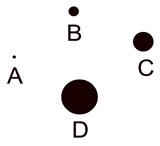
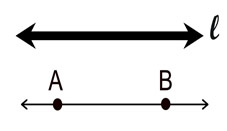
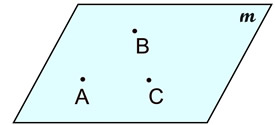
In geometry, formal definitions are formed using other defined words or terms. There are, however, three words in geometry that are not formally defined. These words are point, line and plane, and are referred to as the "three undefined terms of geometry".
Task
Learning Objectives
After this lesson, the student will be able to:
- define and list the characteristics of a point
- describe a line and explain how it is geometrically written
- discuss the geometric shape of a plane
Process
- The student shall discuss one concept he/she know about geometry.
- He/she must acquire a copy of the Undefined Terms of Geometry: Concepts & Significance lesson, then watch the video of it >>> https://study.com/academy/lesson/undefined-terms-of-geometry.html, and pause at 1:50, then start answering the following questions:
- What are undefined terms of geometry?
- Define a point and discuss their purpose.
- Now continue the video, then pause at 3:57, and again answer the following:
- How does the author define a line?
- How are lines labeled?
- What are planes?
- Afterwards, the student answer a short quiz.
I. Multiple Choice
- Which of the following is not an undefined term in geometry?
a. Point b. Line c. Plane d. Set/space e. Quadrilateral
- Which of the following is the correct way of writing a point?
a. P b. {P} c. plane P d. line P e. (P)
- Which shape is used to draw a plane on paper in geometry?
a. Triangles b. Quadrilaterals c.Lines d.Circles e. Points
II. Essay
In not more than 5 sentences, briefly discuss the relationships among the points, lines and planes.
Evaluation
ACTIVITY |
SCORES |
| VIDEOCLIP ACTIVITY | 10 |
| TEST I. | 6 |
| TEST II. | 5 |
Total - 21pts
Notes:
2pts are given to each correct answer in the videoclip activity.
2pts for each item in Test I.
20pts is the standard perfect score with 1pt as a bonus additional score to those who answered all questions satisfactorily.
Conclusion
The 3 "undefined terms in geometry" are the building blocks for the rest of the subject. They are like big cinder blocks that are placed first at the bottom of the house -- without those blocks, the rest of the house can never be built.
While these words are "undefined" in the formal sense, we can still "describe" these words.
The descriptions, stated below, refer to these words in relation to geometry.
|
POINT While we represent a point with a dot, the dot can be very tiny or very large. Remember, a point has no size. |
|
| LINE (straight line) • a line has no thickness. • a line's length extends in one dimension. • a line goes on forever in both directions. • a line has infinite length, zero width, and zero height. • a line is assumed to be straight. • a line is drawn with arrowheads on both ends. • a line is named by a single lowercase script letter, or by any two (or more) points which lie on the line. |
|
| PLANE • a plane has two dimensions. • a plane forms a flat surface extending indefinitely in all directions. • a plane has infinite length, infinite width and zero height (thickness). • a plane is drawn as a four-sided figure resembling a tabletop or a parallelogram. • a plane is named by a single letter (plane m) or by three coplanar, but non-collinear,* points (plane ABC). |
|
SPACE/SET• basic structure in incidence geometry. • consists of a set of elements called points, and a set of elements called lines. • each line is a distinct subset of the points. • the points in a line are said to be incident with the line. |
*Collinear points are points that lie on the same straight line.
*Coplanar points are points that line in the same plane.
Credits
https://study.com/academy/practice/quiz-worksheet-undefined-terms-of-geometry.html
https://study.com/academy/lesson/undefined-terms-of-geometry.html#lesson
https://study.com/academy/lesson/undefined-terms-of-geometry-lesson-plan.html
BUASEN, J.A Plane Geometry. Mathematics-Physics-Statistics Department, College of Arts and Sciences, Benguet State University, La Trinidad, Benguet.